Index
Using the Firewall
Introduction
Developer plan accounts have access to the ModSecurity WAF for each of their sites on a vCanopy managed server. We use the full OWASP foundation 3+ Core Ruleset (CRS) to protect your sites from a wide array of attack vectors including:
- SQL Injection (SQLi)
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Local File Inclusion (LFI)
- Remote File Inclusion (RFI)
- PHP Code Injection
- Java Code Injection
- HTTPoxy
- Shellshock
- Unix/Windows Shell Injection
- Session Fixation
- Scripting/Scanner/Bot Detection
- Metadata/Error Leakages
Using the Firewall
1. PROVISION A SERVER AND DEPLOY A vCanopy SITE
We have documentation on provisioning up and managing servers here:
And documentation about deploying and managing vCanopy sites here:
2. ENABLE/DISABLE THE vCanopy MODSEC WAF
Head over to the Sites page of your vCanopy account, and click on the name of your website to open up the website configuration modal:
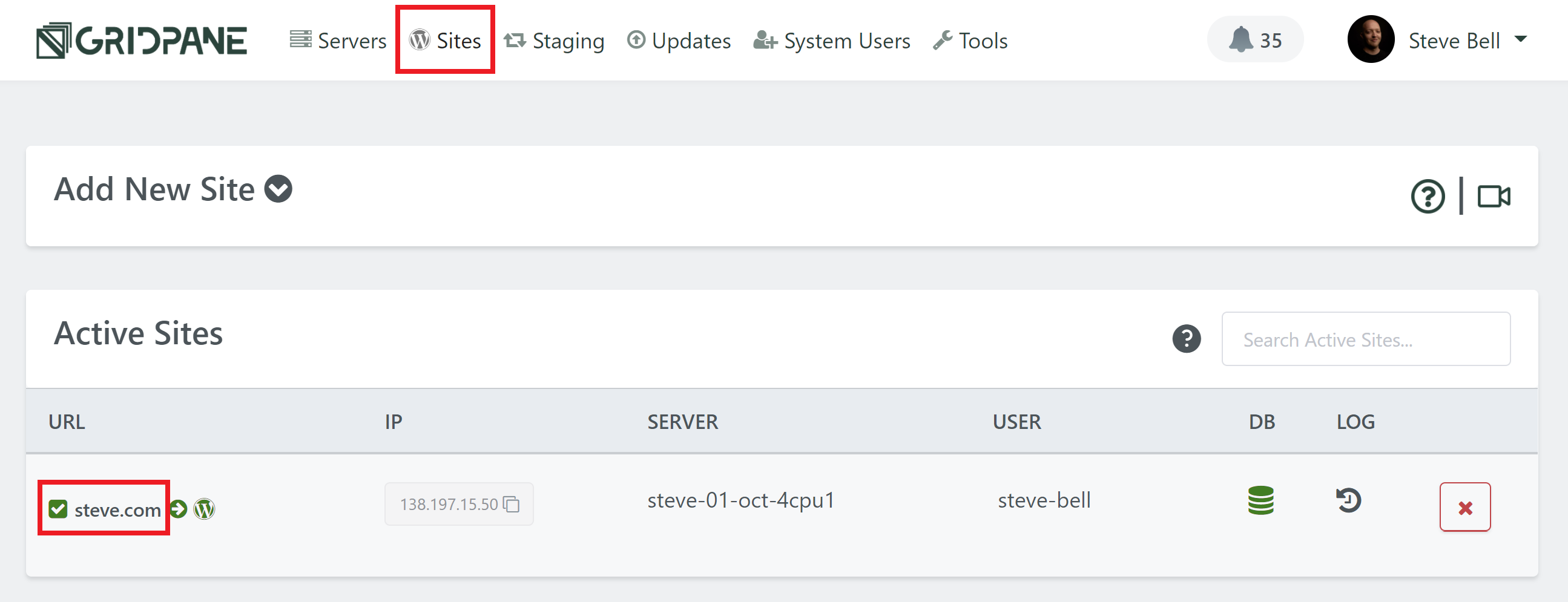
Click through to the security tab and you’ll several different options for securing your websites. Select the ModSec firewall and toggle on the Enable WAF option:
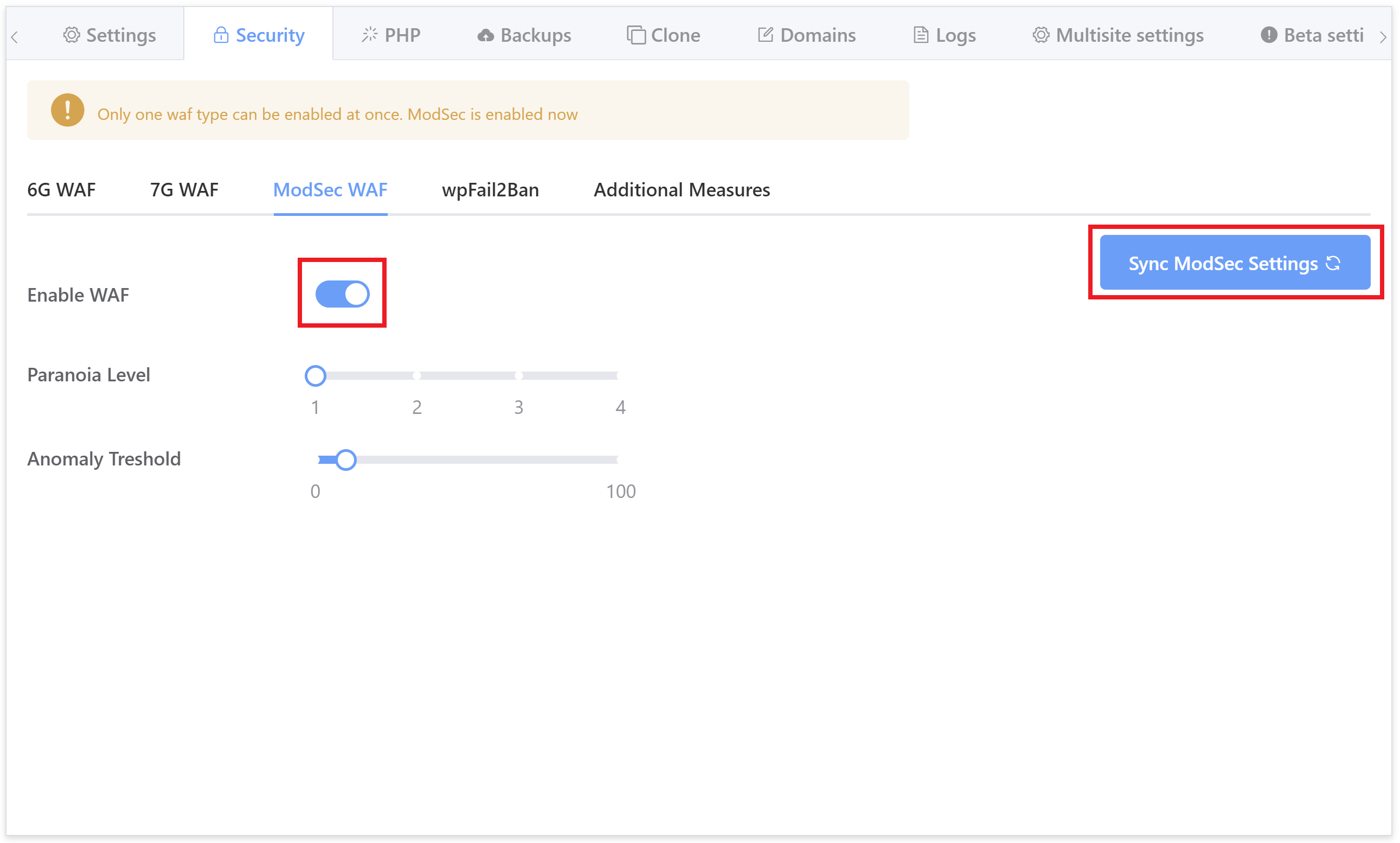
For any existing sites, please also hit the sync button to sync the UI and the server together and bring everything up-to-date. For more information on using the security tab, check out:
Secure Your WordPress Websites: An Overview of the Security Tab
3. ADJUSTING MODSEC WAF SENSITIVITY
The ModSec Waf can be tuned per site by adjusting two of its configuration values, the Paranoia Level and the Anomaly Threshold.
Setting the Paranoia Level
Adjusting the the Modsec paranoia level where {site.url} is your WordPress site’s primary domain and the paranoia level accepts an integer from 1 to 4
gp site {site.url} -modsec -paranoia-level {1-4}The Paranoia Level (PL) setting allows you to choose the desired level of rule checks, the least paranoid level of checking is 1 to the maximum paranoia level of 4.
With each paranoia level increase, the CRS enables additional rules giving you a higher level of security. However, higher paranoia levels also increase the possibility of blocking some legitimate traffic due to false alarms (also named false positives or FPs). If you use higher paranoia levels, it is likely that you will need to add some exclusion rules for certain requests and applications receiving complex input.
Paranoia Level 1 is default. In this level, most core rules are enabled. PL1 is advised for beginners, installations covering many different sites and applications, and for setups with standard security requirements. At PL1 you should face FPs rarely. If you encounter FPs, please open an issue on the CRS GitHub site and don’t forget to attach your complete Audit Log record for the request with the issue.
Paranoia level 2 includes many extra rules, for instance enabling many regexp-based SQL and XSS injection protections, and adding extra keywords checked for code injections. PL2 is advised for moderate to experienced users desiring more complete coverage and for installations with elevated security requirements. Setting Paranoia Level 2 will likely cause some FPs which you will need to handle.
Paranoia level 3 enables more rules and keyword lists, and tweaks limits on special characters used. PL3 is aimed at users experienced at the handling of FPs and at installations with a high-security requirement.
Paranoia level 4 further restricts special characters. The highest level is advised for experienced users protecting installations with very high-security requirements. Running PL4 will likely produce a very high number of FPs which have to be treated before the site can go production live.
Rules in paranoia level 2 or higher will log their PL to the audit log. This allows you to deduct from the audit log how the WAF behavior is affected by the increased paranoia level. for example:
[tag "paranoia-level/2"]
Setting the Anomaly Threshold
Adjusting the Modsec paranoia level where {site.url} is your WordPress site’s primary domain and the paranoia level accepts an integer.
gp site site.com -modsec -anomaly-threshold {integer}The anomaly threshold is where you can specify at which cumulative anomaly score an inbound request,
or outbound response, gets blocked. Most detected inbound threats will give a critical score of 5.
Smaller violations, like violations of protocol/standards, carry lower scores.
vCanopy Default anomaly threshold is set to a value of 10, this means a request would require at least two critical alerts or a combination of many lesser alerts to reach the blocking threshold.
You can adjust this to suit your needs or while tuning the firewall for your site. Setting this value to 5 would result in the firewall blocking any request that gives a single critical score, while a value of 7 would require a critical score plus a smaller violation.
You can increase your threshold to allow for a less secure firewall, however, in such circumstances some attacks may bypass the CRS rules or your own configured policies. Having said that it is a common practice to start a fresh CRS installation with elevated anomaly scoring thresholds (>100) and then lower the limits as your confidence in the setup grows.
ANOMALY THRESHOLD / PARANOIA LEVEL QUADRANT
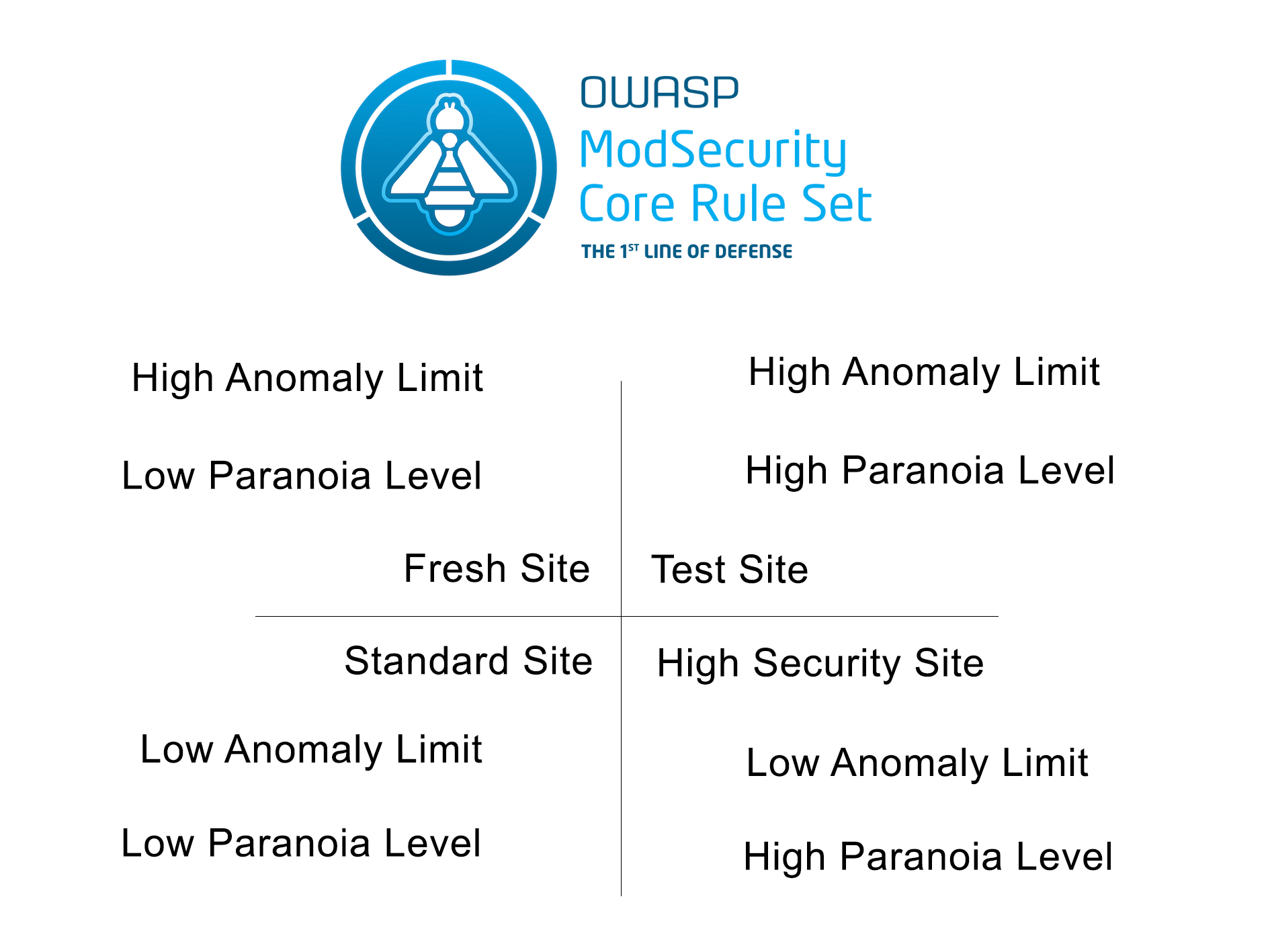
4. MODSEC WAF AUDIT LOGGING
When a request has been blocked by ModSec it will generate an error in the Nginx Error log, available from your logs tab. Here is a typical example, where UptimeRobot user-agent has been blocked:
2019/12/31 16:56:42 [error] 11005#11005: *30442 [client 127.0.0.1] ModSecurity: Access denied with code 403 (phase 1). Matched "Operator `Eq' with parameter `1' against variable `IP:127.0.0.1_1c3991a2733b4c8a7a0286a4800ab4a5a7376e46::::DOS_BLOCK' (Value: `1' ) [file "/etc/nginx/modsec/owasp/rules/REQUEST-912-DOS-PROTECTION.conf"] [line "123"] [id "912130"] [rev ""] [msg ""] [data ""] [severity "0"] [ver ""] [maturity "0"] [accuracy "0"] [tag "application-multi"] [tag "language-multi"] [tag "platform-multi"] [tag "attack-dos"] [hostname "127.0.0.1"] [uri "/"] [unique_id "157892494257.867402"] [ref ""], client: 127.0.0.1, server: an-example.site, request: "HEAD / HTTP/1.1", host: "an-example.site", referrer: "http://an-example.site"
We can see ModSec has blocked this request, the rule that has lead to the block:
[file "/etc/nginx/modsec/owasp/rules/REQUEST-912-DOS-PROTECTION.conf"]
And the rule ID:
[id "912130"]
And importantly the timestamp:
2019/12/31 16:56:42
vCanopy’s ModSec WAF is set up for concurrent logging, this allows for better performance and means each block has an individual report log file in a directory tree structure, with an index of all reports saved to the audit log.
The audit log index can be found on the following site-specific filepath, where {site.url} is replaced by your site’s primary domain:
by SSH:
/var/www/{site.url}/modsec/modsec_audit.logby SFTP
/sites/{site.url}/modsec/modsec_audit.logIn this audit log you will see entries for each block and its relevant report, with the filepath to the report (bold) and some other details of the blocking. We can use the timestamp from the Nginx error log to identify the report we want to investigate.
an-example.site 127.0.0.1 - [31/Dec/2019:16:56:42 +0000] "HEAD / HTTP/1.1" 403 0 https://an-example.site "Mozilla/5.0+(compatible; UptimeRobot/2.0; http://www.uptimerobot.com/)" 157892494257.867402 http://an-example.site /var/www/an-example.site/modsec/audit-logs/audit/20191231/20191231-1656/20191231-165642-157892494257.867402 0 912.000000 md5:961e06ade83aa9d7b76e32cfd0fa2646
In that index line, this is the filepath to the individual log report:
http://an-example.site /var/www/an-example.site/modsec/audit-logs/audit/20191231/20191231-1656/20191231-165642-157892494257.867402
We can view the log in our terminal:
cat /var/www/an-example.site/modsec/audit-logs/audit/20191231/20191231-1656/20191231-165642-157892494257.867402
And get the full report:
---uGAklyhg---A-- [31/Dec/2019:16:56:42 +0000] 157892494257.867402 127.0.0.1 39814 127.0.0.1 8080 ---uGAklyhg---B-- HEAD / HTTP/1.1 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0+(compatible; UptimeRobot/2.0; http://www.uptimerobot.com/) X-Forwarded-Proto: https Connection: close X-Original-Host: an-example.site X-Forwarded-For: 63.143.42.243 X-Real-IP: 63.143.42.243 Content-Length: 0 X-Original-Scheme: https accept-encoding: gzip, deflate HTTPS: on Referer: http://an-example.site Host: an-example.site Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 cache-control: no-cache Accept-Language: en-US,en;q=0.8 Accept-Charset: ISO-8859-1,UTF-8;q=0.7,*;q=0.7 ---uGAklyhg---D-- ---uGAklyhg---F-- HTTP/1.1 403 Server: nginx Date: Mon, 31 Dec 2019 16:56:42 GMT Content-Length: 146 Content-Type: text/html Connection: close ---hyHQa6IL---H-- ---hyHQa6IL---I-- ---hyHQa6IL---J-- ---hyHQa6IL---Z--
You can find more details on the sections of a report and their different possible content in the ModSecurity handbook here.
5. ADDING EXCEPTIONS AND WHITELISTS TO TUNE THE CORE RULESET
OWASP Core Rule Set (CRS) as a rule set for ModSecurity has no context into what your web application is doing and how it is designed. As a result, often legitimate requests might seem to CRS to be attacks. This term is often called a False Positive. While the CRS team does its best to prevent these from happening, they are somewhat inevitable due to the blacklist nature of the rules.
Because of this the ModSec firewall CRS can be tuned with exceptions and whitelists, more details can be found at the ModSec Core Ruleset documentation here.
Exceptions versus Whitelist
There are two generally different methods for modifying rules. Exceptions, which will remove or modify the rule from startup time and whitelist modifications which can modify a rule based on the content of a transaction. In general whitelist rules are slightly more powerful but also more expensive as they must be evaluated every time a transaction comes in.
You can create serverwide exceptions that will work across all sites by putting your rules in this file on the server, it will load these up before loading in the security rules:
/etc/nginx/modsec/owasp/rules/REQUEST-900-EXCLUSION-RULES-BEFORE-CRS.conf
Alternatively, you can create site specific exceptions and whitelists using the following two files, replacing {site.url} with your site’s primary domain:
/var/www/{site.url}/modsec/{site.url}-runtime-exceptions.conf
/var/www/{site.url}/modsec/{site.url}-runtime-whitelist.conf Adding a whitelist rule
In the above logging example we saw that the firewall was blocking Uptime Robot. We have the ID of the rule that was triggering the block, 912130, and in the report we have a bunch of detail we can use to whitelist these requests.
We could target the User-Agent, but this is easy to spoof, so instead we are going to use the X-Real-IP that has been passed through to the Nginx backend from our reverse proxy. We can confirm that the IP 63.143.42.243 belongs to UptimeRobot and then check the REQUEST_HEADERS for this value.
Add a rule in the /var/www/{site.url}/modsec/{site.url}-runtime-whitelist.conf like so:
SecRule REQUEST_HEADERS:X-Real-IP "@Contains 63.143.42.243" "id:3, phase:1, nolog, allow, pass, ctl:ruleRemoveById=912130"
Please note the highlighted ID above. All rules and exceptions you add must have a unique numerical ID. If you are adding rules in site-specific locations, please ensure that you increment your rule IDs. All vCanopy servers come with two rules for whitelisting Gutenberg/JSON API calls, which are id:1 and id:2 – please make sure to increment your rules from 3+.
Check Nginx syntax and reload:
gp ngx -t && gp ngx reload
So now when the Firewall detects a request is coming from the Uptime Robot Real IP it removes the rule that was preventing the external resources from connecting to the site, in this case 912130 is an anti aa-dos rule.