UPDATE
Options for customizing PHP on your individual websites are now available directly inside the UI in your site customiser!
We highly recommend you use the new tab inside your vCanopy account dashboard to make any PHP changes you need, but the GP CLI detailed below is all still correct for everyone who prefers working via CLI.
You can open up your site customizer by clicking the domain name of site inside the Sites page of your vCanopy account.
PHP settings are inside the PHP tab. Before you can make changes you may need to sync your settings. You can do this by clicking the Sync PHP Settings button:

Index
- allow_url_fopen
- allow_url_include
- date.timezone
- default_socket_timeout
- max_execution_time
- max_files_upload
- max_input_time
- max_input_vars
- memory_limit
- post_max_size
- session.cookie_lifetime
- session.gc_maxlifetime
- short_open_tag
- upload_max_filesize
Configure PHP Opcache by Version
- opcache.enable
- opcache.enable_cli
- opcache.memory_consumption
- opcache.max_accelerated_files
- opcache.revalidate_freq
- date.timezone
- default_socket_timeout
- max_execution_time
- max_files_upload
- max_input_time
- max_input_vars
- memory_limit
- post_max_size
- session.cookie_lifetime
- session.gc_maxlifetime
- short_open_tag
- upload_max_filesize
Configure PHP Process Manager/Workers by Site
- pm
- pm.max_children
- pm.max_requests
- pm.max_spare_servers
- pm.min_spare_servers
- pm.process_idle_timeout
- pm.start_servers
How Your Site PHP Workers… work
Configure PHP by Version
These changes are recorded in each PHP versions php.ini which resides at the following filepath, replacing {php.version} with the version of PHP required:
/etc/php/{php.version}/fpm/php.iniSettings configured in aphp.iniare global by nature and impact each WordPress site which uses that particular version of PHP, unless that site has a conflicting per site .user.ini setting, in which case the per-site configuration takes precedence.
In each command below, substitute your PHP version (7.2, 7.3, etc) in place of {php.version}.
Each command automatically reloads the requisite PHP version, however, if you are wishing to chain together several commands you may wish to use the -no-reload flag as the last argument. This will stop you from reloading PHP multiple times, after which you can reload php.
For example:
gp stack php 7.4 -mem-limit 512 -no-reload && gp stack php 7.4 -max-exec-time 60 -no-reload && gp php 7.4 reload
PHP Version General Settings
These commands all take integer arguments, with the integer being converted into the required unit by the script. and impact all WordPress sites using that version of PHP.
ALLOW URL-AWARE FOPEN WRAPPERS.
Enable URL-aware fopen wrappers that enable accessing URL objects like files.
Directive: allow_url_fopen
Default value: on
Accepted values: Boolean/on/off/On/Off/ON/OFF
gp stack php {php.version} -allow-url-fopen {accepted.value}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -allow-url-fopen on
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the PHP version level.
ALLOW URL-AWARE FOPEN WRAPPERS WITH INCLUDE FUNCTIONS.
Allows the use of URL-aware fopen wrappers with the following functions:
include, include_once, require, require_once
Directive: allow_url_include
Default value: off
Accepted values: Boolean/on/off/On/Off/ON/OFF
Requires: allow_url_fopen = on
gp stack php {php.version} -allow-url-include {accepted.value}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -allow-url-include on
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the PHP version level.
SET THE DEFAULT TIMEZONE USED BY ALL DATE/TIME FUNCTIONS.
Sets The default timezone used by all date/time functions. The precedence order for which timezone is used if none is explicitly mentioned is described in the date_default_timezone_get() page at php.net. Please check this list of supported timezones at php.net.
Directive: date.timezone
Default value: NULL
Accepted Values: {supported.timezone} (String)
gp stack php {php.version} -date-timezone {supported.timezone}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -date-timezone Pacific/Honolulu
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE SOCKET/STREAM WAIT TIMEOUT FOR A PHP SCRIPT.
The socket/stream wait time is not included in PHPs max execution time. The default socket timeout in PHP is 60 seconds. HTTP requests performed with some functions may exceed the execution time due to this wait being too short. Examples of such functions include:
file_get_contents, fopen or curl
Directive: default_socket_timeout
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 60
gp stack php {php.version} -default-socket-timeout {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -default-socket-timeout 300
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE MAXIMUM EXECUTION TIME FOR EACH PHP SCRIPT.
Set the maximum time in seconds a script is allowed to run before it is terminated by the parser.
Directive: max_execution_time
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 300
gp stack php {php.version} -max-exec-time {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -max-exec-time 300
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE MAXIMUM NUMBER OF FILES THAT CAN BE UPLOAD VIA A SINGLE REQUEST BY A PHP SCRIPT.
The maximum number of files allowed to be uploaded simultaneously. Upload fields left blank on submission do not count towards this limit.
Directive: max_files_upload
Unit: Files
Default value: 20
gp stack php {php.version} -max-file-uploads {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -max-file-uploads 1024
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE MAXIMUM INPUT TIME FOR EACH PHP SCRIPT.
Set the maximum time in seconds a script is allowed to parse input data, like POST and GET. Timing begins at the moment PHP is invoked at the server and ends when execution begins. Set to 0 to allow unlimited time.
Directive: max_input_time
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 60
gp stack php {php.version} -max-input-time {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -max-input-time 120
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET HOW MANY GET/POST/COOKIE INPUT VARIABLES MAY BE ACCEPTED BY A PHP SCRIPT.
How many input variables may be accepted (limit is applied to $_GET, $_POST and $_COOKIE superglobal separately). Use of this directive mitigates the possibility of denial of service attacks that use hash collisions.
Directive: max_input_vars
Unit: Variables
Default value: 5000
gp stack php {php.version} -max-input-vars {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -max-input-vars 10000
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE MAXIMUM POST SIZE PER PHP SCRIPT.
Sets max size of post data allowed. To upload large files, this value must be larger than upload_max_filesize. Generally speaking, this should also be smaller than the set memory_limit.
Directive: post_max_size
Unit: MB
Default value: 512
gp stack php {php.version} -post-max-size {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -post-max-size 1024
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE MEMORY LIMIT FOR EACH PHP SCRIPT
Set the maximum amount of memory that a script is allowed to allocate. This helps prevent poorly written scripts for eating up all available memory on a server. Note that to have no memory limit, set this directive to -1.
Directive: memory_limit
Unit: MB
Default value: 256
gp stack php {php.version} -mem-limit {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -mem-limit 512
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE SESSION COOKIE LIFETIME FOR A COOKIE CREATED BY A PHP SCRIPT.
Specify the lifetime of a cookie in seconds which is sent to the browser. The value 0 means “until the browser is closed.”
Directive: session.cookie_lifetime
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 0
gp stack php {php.version} -session-cookie-lifetime {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -session-cookie-lifetime 3600
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE GARBAGE COLLECTION FOR DATA CREATED BY A PHP SCRIPT.
Specify the number of seconds after which data will be seen as ‘garbage’ and potentially cleaned up.
Directive: session.gc_maxlifetime
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 1440
gp stack php {php.version} -session-gc-maxlifetime {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -session-gc-maxlifetime 3600
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
ENABLE THE SHORT FORM OF PHP’S OPEN TAG.
Tells PHP whether the short form <? ?> of PHP’s open tag should be allowed. Disabled by default, so it is possible to use PHP in combination with XML inline <? xml ?>. If you enable this option and have difficulties with xml inline, please remember to echo the XML'; ?>.
Directive: short_open_tag
Accepted values: on | off
Default value: off
gp stack php {php.version} -short-open-tag {on.off}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -short-open-tag on
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
SET THE MAXIMUM UPLOAD FILE SIZE EACH PHP SCRIPT ALLOWS.
Set the maximum size allowed for an uploaded file by a PHP script.
Directive: upload_max_filesize
Unit: MB
Default value: 512
gp stack php {php.version} -upload-max-filesize {integer}Example:
gp stack php 7.4 -upload-max-filesize 1024
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
Configure PHP Version OPcache Settings
OPcache provides an improvement to PHP performance by storing precompiled script bytecode in shared memory, thereby removing the need for PHP to load and parse scripts on each request.
ENABLE/DISABLE OPCACHE
Directive: opcache.enable
Default value: enabled
gp stack php {php.version} -opcache-enable
gp stack php {php.version} -opcache-disableExample:
gp stack php 7.4 -opcache-enable
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set by gp-cli at the PHP version level.
ENABLE/DISABLE CLI
Directive: opcache.enable_cli
Default value: disabled
(primarily used for debugging issues with OPcache itself, not suitable for most users)
gp stack php {php.version} -opcache-enable-cli
gp stack php {php.version} -opcache-disable-cliExample:
gp stack php 7.4 -opcache-enable-cli
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the PHP version level.
SET THE NUMBER OF OPCACHE ACCELERATED FILES
This is the maximum number of keys (and therefore scripts) in the OPcache hash table. The larger the number, the more scripts that will be hashed. Although you set the value, the actual value which will be used is the first number in the set of prime numbers { 223, 463, 983, 1979, 3907, 7963, 16229, 32531, 65407, 130987 } that is greater than or equal to the configured value. The minimum value is 200, default is 10000, and maximum is 1000000 in PHP 7.x.
Directive: opcache.max_accelerated_files
Unit: MB
Default value: 10000
gp stack php {php.version} -opcache-max-accel-files {integer}Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the PHP version level.
SET AN OPCACHE MEMORY LIMIT
Change the size of the shared memory storage used by OPcache, in megabytes.
Directive: opcache.memory_consumption
Unit: MB
Default value: 64
gp stack php {php.version} -opcache-memory {integer}Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the PHP version level.
SET THE OPCACHE REVALIDATION FREQUENCY
This value determines who often to check script timestamps for updates and it expressed in seconds. A value of 0 will result in OPcache checking for updates with every request. The default value is 60.
Directive: opcache.revalidate_freq
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 60
gp stack php {php.version} -opcache-reval-freq $intOptional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the PHP version level.
Configure PHP by site
These settings only impact the site for which they are set. The changes are written to a.user.ini which resides at the following filepath:
/var/www/{site.url}/htdocs/.user.ini(by SSH/SFTP as root)
/Sites/{site.url}/htdocs/.user.ini(by SSH/SFTP as system user)
In each command below, substitute your site for {site.url}.
Each command automatically reloads the requisite PHP version for that site, however if you are wishing to chain together several commands you may wish to use the -no-reload flag as the last argument. This will stop you from reloading PHP multiple times, after which you can reload php.
For example:
gp stack php -site-mem-limit 512 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp stack php -site-max-exec-time 60 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp php 7.4 reload
Site PHP General Settings
These commands all take integer arguments, with the integer being converted into the required unit by the script. and impact all WordPress sites using that version of PHP.
You may notice many of these commands will configure the parameters identical to those at the PHP version level. As noted below each script that is affected, configuring these parameters at a site level will take precedence over the values set at the PHP version level.
SET THE DEFAULT TIMEZONE USED BY ALL DATE/TIME FUNCTIONS.
Sets The default timezone used by all date/time functions. The precedence order for which timezone is used if none is explicitly mentioned is described in the date_default_timezone_get() page at php.net. Please check this list of supported timezones at php.net.
Directive: date.timezone
Default value: NULL
Accepted Values: {supported.timezone} (String)
gp stack php -site-date-timezone {supported.timezone} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-date-timezone Pacific/Honolulu vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the timezone for your individual sites in your customizer here:

SET THE SOCKET/STREAM WAIT TIMEOUT FOR A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT.
The socket/stream wait time is not included in PHPs max execution time. The default socket timeout in PHP is 60 seconds. HTTP requests performed with some functions may exceed the execution time due to this wait being too short. Examples of such functions include:
file_get_contents, fopen or curl
Directive: default_socket_timeout
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 60
gp stack php -site-default-socket-timeout {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-default-socket-timeout 300 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the default socket timeout for your individual sites in the site customizer here:

SET THE MAXIMUM EXECUTION TIME FOR A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT.
Set the maximum time in seconds a site’s PHP script is allowed to run before it is terminated by the parser.
Directive: max_execution_time
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 300
gp stack php -site-max-exec-time {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-max-exec-time 300 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the max execution time for your individual sites here:

SET THE MAXIMUM NUMBER OF FILES THAT CAN BE UPLOAD VIA A SINGLE REQUEST BY A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT.
The maximum number of files allowed to be uploaded simultaneously. Upload fields left blank on submission do not count towards this limit.
Directive: max_files_upload
Unit: Files
Default value: 20
gp stack php -site-max-file-uploads {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-upload-max-filesize 1024 {site.url}Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the maximum number of files that can be uploaded for your individual sites inside your site customizer here:

SET THE MAXIMUM INPUT TIME FOR A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT.
Set the maximum time in seconds a site’s PHP script is allowed to parse input data, like POST and GET. Timing begins at the moment PHP is invoked at the server and ends when execution begins. Set to 0 to allow unlimited time.
Directive: max_input_time
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 60
gp stack php -site-max-input-time {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-max-input-time 120 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the maximum input time for your individual sites inside your customizer here:

SET HOW MANY GET/POST/COOKIE INPUT VARIABLES MAY BE ACCEPTED BY A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT.
How many input variables may be accepted (limit is applied to $_GET, $_POST and $_COOKIE superglobal separately). Use of this directive mitigates the possibility of denial of service attacks that use hash collisions.
Directive: max_input_vars
Unit: Variables
Default value: 5000
gp stack php -site-max-input-vars {site.ur;} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-max-input-vars 10000 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the max input variables for your individual sites in your customizer here:

SET THE MEMORY LIMIT FOR A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT
Set the maximum amount of memory that any site’s PHP script is allowed to allocate. This helps prevent poorly written scripts for eating up all available memory on a server. Note that to have no memory limit, set this directive to -1.
Directive: memory_limit
Unit: MB
Default value: 256
gp stack php -site-mem-limit {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-mem-limit 512 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the memory limit for each of your individual sites in your customizer here:

SET THE MAXIMUM POST SIZE PER PHP SCRIPT.
Sets max size of post data allowed. To upload large files, this value must be larger than upload_max_filesize. Generally speaking, this should also be smaller than the set memory_limit.
Directive: post_max_size
Unit: MB
Default value: 512
gp stack php -site-post-max-size {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-post-max-size 1024 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the maximum post size for your individual sites in your customizer here:

SET THE SESSION COOKIE LIFETIME FOR A COOKIE CREATED BY A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT.
Specify the lifetime of a cookie in seconds which is sent to the browser. The value 0 means “until the browser is closed.”
Directive: session.cookie_lifetime
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 0
gp stack php -site-session-cookie-lifetime {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-session-cookie-lifetime 3600 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
You can set the session cookie lifetime for your individual sites in your customizer here:

SET THE GARBAGE COLLECTION FOR DATA CREATED BY A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT.
Specify the number of seconds after which data will be seen as ‘garbage’ and potentially cleaned up.
Directive: session.gc_maxlifetime
Unit: Seconds
Default value: 1440
gp stack php -site-session-gc-maxlifetime {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-session-gc-maxlifetime 3600 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set on a per-site level. Any per-site configuration will supersede this configuration.
You can set the garbage collection lifetime for your individual sites in your site customizer here:

ENABLE THE SHORT FORM OF PHP’S OPEN TAG.
Tells PHP whether the short form <? ?> of PHP’s open tag should be allowed. Disabled by default, so it is possible to use PHP in combination with XML inline <? xml ?>. If you enable this option and have difficulties with xml inline, please remember to echo the XML'; ?>.
Directive: short_open_tag
Accepted values: on | off
Default value: off
gp stack php -site-short-open-tag {on.off} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-short-open-tag on vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can enable PHP’s short open tag for your individual websites with this toggle inside your site customizer:

SET THE MAXIMUM UPLOAD FILE SIZE A SITE’S PHP SCRIPT ALLOWS.
Set the maximum size allowed for an uploaded file by a site’s PHP script.
Directive: upload_max_filesize
Unit: MB
Default value: 512
gp stack php -site-upload-max-filesize {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-upload-max-filesize 1024 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive may also be set at the PHP version level. This site level setting will take precedence over any PHP version level setting.
You can set the maximum upload file size for your individual sites in your customizer here:

PHP by Site – Process Manager/Workers
These settings allow you to manipulate how your PHP workers behave per site. The PHP version of your site is automatically detected and settings created are stored in a PHP pool {site.url}.conf:
/etc/php/{php.version}/fpm/pool.d/{site.url}.conf.It’s important to note, only the settings configured using gp-cli will persist when you change PHP versions of your site. Any other configurations added to this file manually will be lost when a site’s PHP version is changed. If you do manually edit these files, please make a copy so you can reapply any additional manually configured parameters again after a PHP version switch.
In each command below, substitute your site for {site.url}.
Each command automatically reloads the requisite PHP version for that site, however, if you are wishing to chain together several commands you may wish to use the -no-reload flag as the last argument. This will stop you from reloading PHP multiple times, after which you can reload PHP.
For example:
gp stack php -site-pm static vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp stack php-site-pm-max-children 20 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp php 7.4 reload
SET THE SITE’S PHP PROCESS MANAGER TYPE.
Here are three ways to make PHP work: ondemand, static, & dynamic.
- Ondemand is where PHP workers are fired up as requested, but it is possible to have no PHP workers in existence.
- Static is where you set a finite amount of workers to be active at all times.
- Dynamic is a bit like both where you can set a minimum and a maximum number of workers. PHP workers are generated when needed, with a minimum number set.
Directive: pm
Default value: dynamic
Accepted Values: ondemand / static / dynamic
gp stack php -site-pm {accepted.value} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-pm static vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the site level. You can set this inside your sites customizer here:

CONFIGURE THE SITE’S MAXIMUM PHP WORKERS – ONDEMAND / STATIC / DYNAMIC
The number of child processes to be created when pm is set to static and the maximum number of child processes when pm is set to dynamic or ondemand. This value sets the limit on the number of simultaneous requests that will be served.
Our defaults on newly created servers are 4 workers per CPU core. So for 2 core server, your defaults will be 8 workers (2 x 4), on a 4 core server, it would be 16 (4 x 4).
Directive: pm.max_children
Default value: 4 x CPU Core
Accepted Values: integer
gp stack php -site-pm-max-children {accepted.value} {site.url}Example for a 2 CPU server:
gp stack php -site-pm-max-children 8 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the site level. You can change this in your site customizer here:

CONFIGURE A SITE’S PHP PROCESS MANAGER MAX REQUESTS
This command will allow you to set how many requests the PHP process can take before it is recycled. It can be useful if the app has a memory leak. The default value is 500. Use this command to change that value:
Directive: pm.max_requests
Default value: 500
Accepted Values: integer
gp stack php -site-pm-max-requests {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php-site-pm-max-requests 300 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the site level. You can change this in your site customizer here:

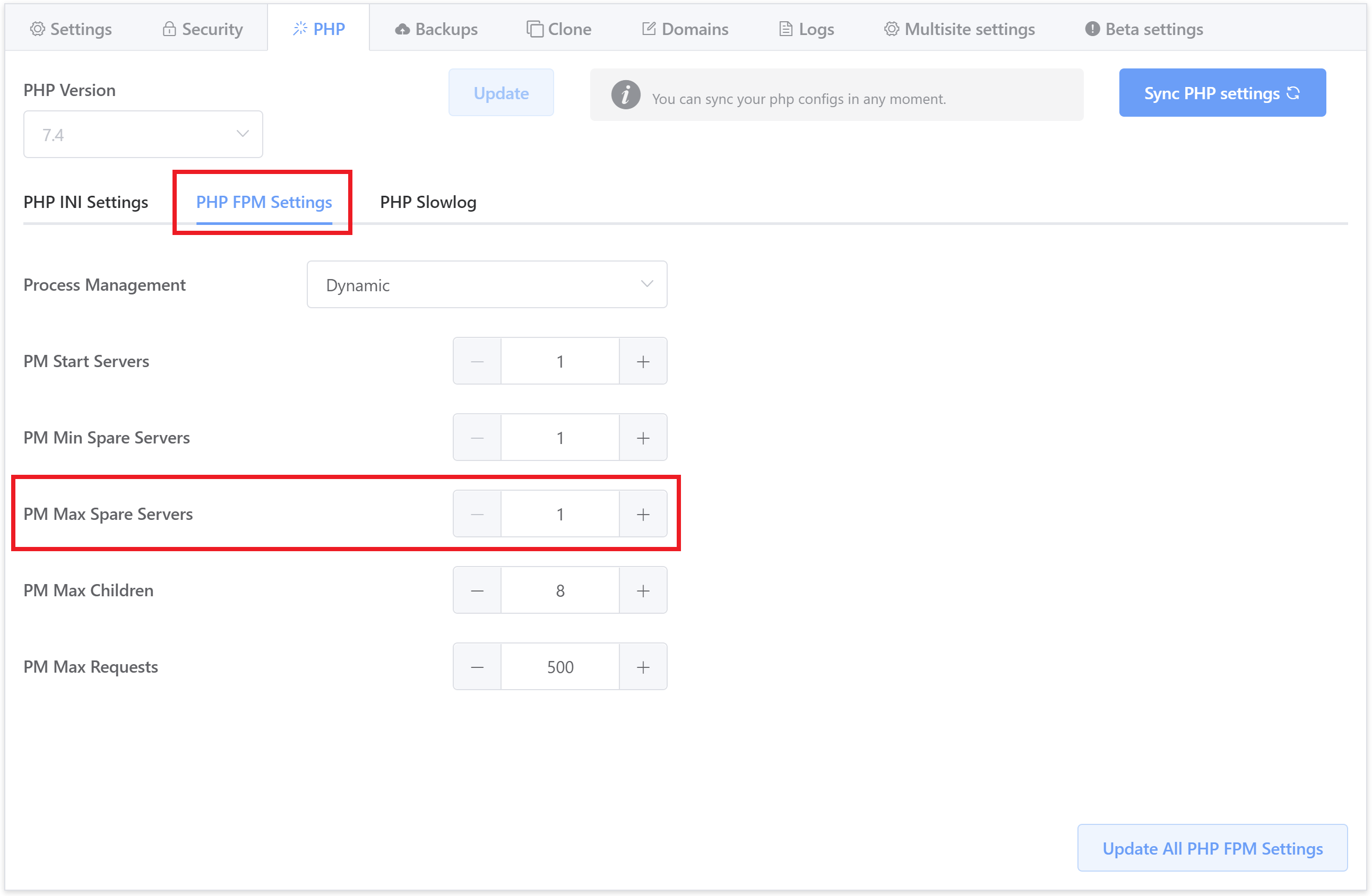
CONFIGURE A SITE’S DYNAMIC PHP MAXIMUM SPARE WORKERS
Set the maximum number of children in ‘idle’ state (waiting to process) workers. If the number of ‘idle’ processes is greater than this number then some children will be killed.
Note: Used only when pm is set to dynamic and is mandatory.
Directive: pm.max_spare_servers
Default value: 1
Accepted Values: integer
gp stack php -site-pm-max-spare-servers {accepted.value} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-pm-max-spare-servers 4 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the site level. You can change this in your site customizer here:
CONFIGURE A SITE’S DYNAMIC PHP MINIMUM SPARE WORKERS
Set the maximum number of children in ‘idle’ state (waiting to process) workers. If the number of ‘idle’ processes is less than this number then some children will be created.
Note: Used only when pm is set to dynamic and is mandatory.
Directive: pm.min_spare_servers
Default value: 1
Accepted Values: integer
gp stack php -site-pm-min-spare-servers {accepted.value} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-pm-min-spare-servers 4 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the site level. You can change this in your site customizer here:

CONFIGURE A SITE’S ONDEMAND PHP IDLE PROCESS TIMEOUT
Set the number of seconds after which an idle process will be killed.
Note: Used only when pm is set to ondemand.
Directive: pm.process_idle_timeout
Default value: 10
Accepted Values: integer
gp stack php -site-pm-process-idle-timeout {integer} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-pm-process-idle-timeout 4 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the site level. You can change this in your site customizer here:

CONFIGURE A SITE’S DYNAMIC PHP STARTING WORKERS
Set the number of children created on startup when process management is set to Dynamic.
Note: Used only when pm is set to dynamic and is mandatory.
Directive: pm.start_servers
Default value: 1
Accepted Values: integer
gp stack php -site-pm-start-servers {accepted.value} {site.url}Example:
gp stack php -site-pm-start-servers 2 vCanopy.com
Optional last flag: -no-reload
This directive can only be set at the site level. You can change this in your site customizer here:

How Your Site PHP Workers… Work
The process manager will control the number of child processes.
STATIC
If you choose static, then there will always be PHP workers in existence no matter whether the application is active or not. This results in a higher resource footprint but can lead to increased performance when resources are plentiful as there is no wasted time in spinning processes up or down. It is important to manage workers against resources such as PHP memory when choosing this mode.
Given PHP is single-threaded it is often recommended to run from 1-2x as many Static PHP workers as you have threads available.
For that reason, you’ll want to set a maximum number of workers at the same time. Because our default is 100 workers, if you choose static without also setting the maximum, you’ll likely bring your whole server down in a short period of time. (unless you have a monster server)
It’s useful to string them together to avoid forgetting. This example sets the workers to 8, sets the site to static, and then reloads PHP 7.4:
gp stack php -site-pm-max-children 8 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp stack php -site-pm static vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp php 7.4 restart
DYNAMIC
If you choose dynamic, then you will not only be setting the maximum number of workers, but you will also need to set the minimum and maximum number of idle workers. It’s also a good idea to set the starting servers which will set the number of servers active when PHP starts up – giving it time to adjust up or down as needed.
Again, it’s useful to string them together to avoid forgetting. This example sets the maximum number of workers to 30, with 20 as the starting number, 10 as minimum idle, and 20 as maximum idle.
gp stack php -site-pm-max-children 30 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp stack php -site-pm-start-servers 20 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp stack php -site-pm-min-spare-servers 10 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp stack php -site-pm-max-spare-servers 20 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp php 7.4 restart
ONDEMAND
If you choose ondemand, then there can be no PHP processes, with the server just spinning them up when needed. In this mode, you can set the maximum number of workers, but it is also important to set the amount of time after which idle processes can be killed.
Once again, it’s useful to string them together to avoid forgetting. This example sets the maximum number of workers to 100, with the idle timeout to 10 seconds.
gp stack php -site-pm-max-children 100 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp stack php -site-pm-process-idle-timeout 10 vCanopy.com -no-reload && gp php 7.4 restart

Further Reading
If you’d like to learn more about PHP workers we have an in-depth blog post that digs into the topic. You can check it out here:
