Introduction
vCanopy Nginoil is an optional feature that runs as a part of the nginx.service on startup. Unlike a regular start-up that runs a standard nginx -t, Nginoil has built-in functionality to detect where Nginx syntax errors are originating from and then, where possible, implement a fix that allows Nginx to successfully boot up.
This means that one “broken” site won’t keep all the other sites on the server from successfully coming online.
Below we’ll take a look at how Nginoil works and how to activate it.
Table of Contents
About vCanopy Nginoil
When activated, Nginoil will run as a part of the “Nginx start systemd” service. Nginoil is a drop-in replacement for the standard nginx -t that takes place when nginx.service runs to start/restart the Nginx service.
What it Does
With Nginoil active, now your server will still run a syntax check, but now if any errors are detected it will try to repair them in order to bring Nginx online.
What it Doesn’t Do
Nginoil won’t fix your mistakes or errors in configuration files, for example, if you’ve edited an Nginx configuration file it won’t find and automatically resolve code errors there. You will still need to fix any syntax errors should they occur.
How it Works
Nginoil runs when the Nginx service starts. If Nginx has no errors it starts as normal. If a syntax error is detected, the following occurs:
- Tests the main /etc/nginx.conf without virtual servers. If there’s still an issue, it won’t be able to heal this, and so it will send you notifications.
- Checks for broken symlinks in /etc/nginx/sites-enabled and removes them if they exist.
- Checks through each site on the server for Nginx syntax errors and if found removes their symlink from /etc/nginx/sites-enabled.
This means that any sites with broken Nginx configurations will remain down, but Nginx and all other healthy websites will come online.
Any changes made are logged to /opt/vCanopy/apply.nginoil and notifications are sent to the application and Slack throughout the process to inform you of what has taken place.
Are There Any Disadvantages to Using Nginoil?
When Nginoil is enabled, it will only remove Nginx virtual servers that are causing issues when Nginx restarts.
That will only happen if one of two things occur:
- The server is restarting (security update reboot or manual).
- Some has decided to restart/stop/start Nginx manually.
Restarting Nginx when you have syntax errors brings Nginx down. Nginx won’t start if there are syntax errors, and if Nginx won’t start, all of the websites on your server will go offline.
If Nginoil is active, and the errors are solely due to configs at a site specific level, then Nginoil will remove those sites virtual server symlinks (nothing more destructive), and then Nginx would start.
In this scenario, only the site/s with Nginx config errors are offline.
To summarise, there are only disadvantages to NOT using Nginoil.
Fixing Site/s That Nginoil Removes
As Nginoil only removes the symlink, you can still use our CLI to run a syntax check against the specific site/s. This will show you the error so that it may be investigated and resolved, and then putting the symlink back is simple – it’s just adding another flag to the CLI. All details can be found below.
Activation (and Deactivation)
You can enable Nginoil directly inside your vCanopy account or via GP-CLI.
Enable/Disable via Server Toggle
Head over to the servers page inside your vCanopy account and click on the name of the server you wish to activate Nginoil on:
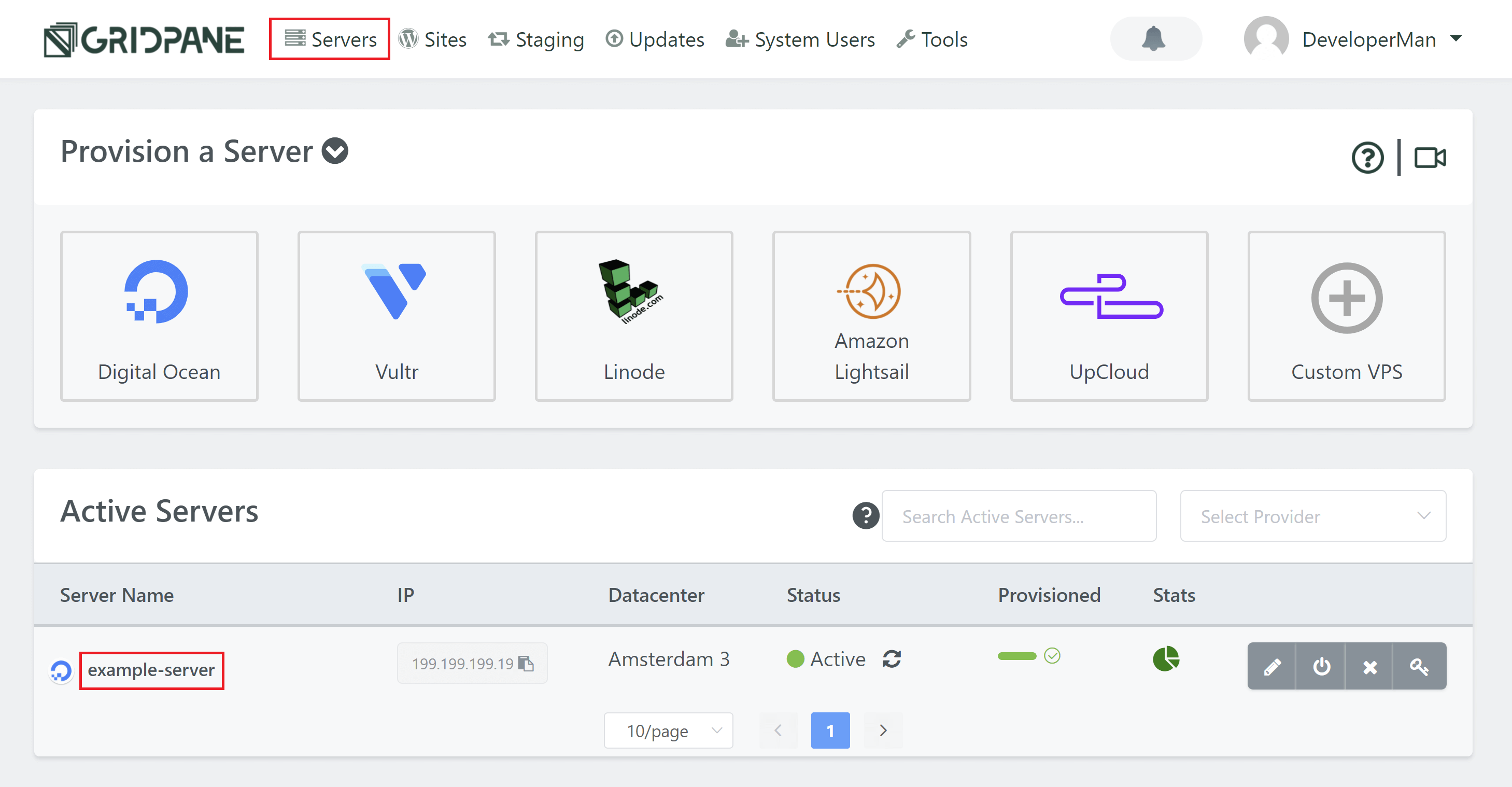
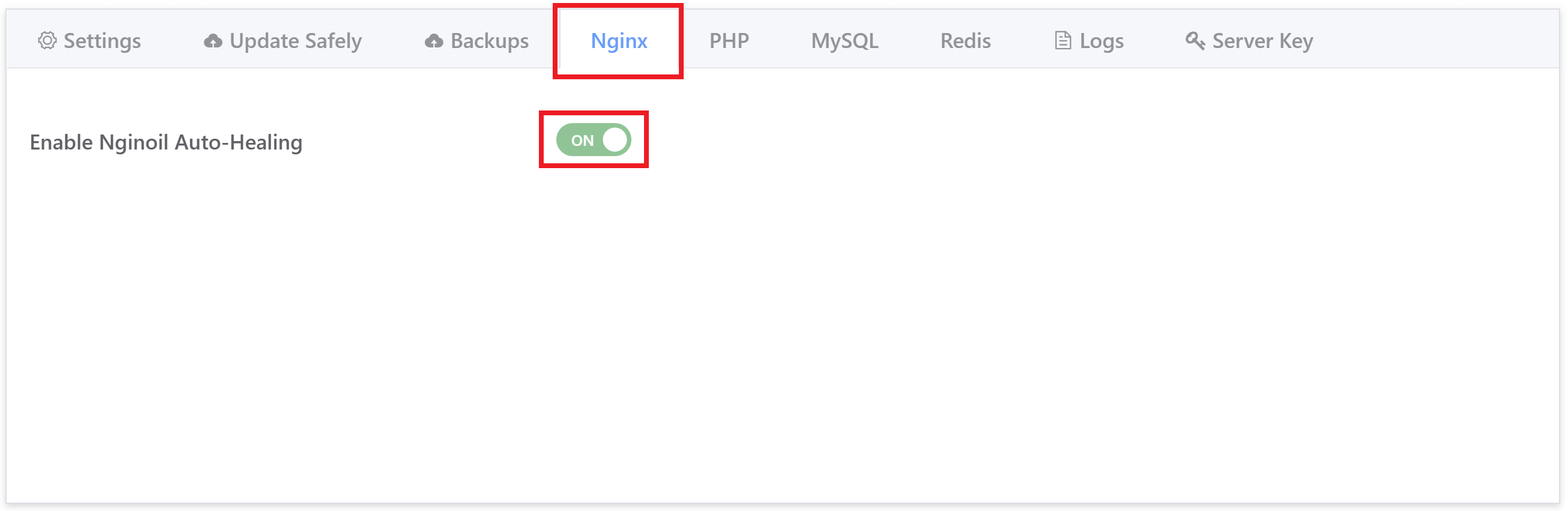
This will open up the website customizer. Click through to the Nginx tab, and here you’ll find the toggle to activate or deactivate Nginoil:
Enable/Disable via GP-CLI
You can enable or disable Nginoil with the following commands:
gp stack nginx -enable-nginoil gp stack nginx -disable-nginoil
This creates a token file in the /opt/vCanopy directory:
/opt/vCanopy/apply.nginoil
And it adds a boolean value to /root/gridenv/nginx.env. You can confirm
nginoil:true||false
With this active, Nginoil auto-healing functions are live.
vCanopy Nginoil CLI
Nginoil itself is a command that you can run on your servers. However, you should exercise caution when running this command manually.
nginoil
This will run an gp nginx -t followed by the auto-repair functions built in if an error is present. This means that if you’ve just edited a file and that has caused an Nginx syntax error, Nginoil would remove the symlink for this site, taking it site offline.
This will also log the actions that have been taken, and send a notification to your account and to Slack (if enabled), letting you know what’s occurred.
Warning
As already mentioned, you should exercise caution when using this command. If you've just added/edited a custom site-specific config and there's now a syntax error, you can still undo or fix the mistake to resolve this without taking the site offline unnecessarily.
Nginoil Event Log
Any actions taken by Nginoil are logged in the following custom log:
/opt/vCanopy/apply.nginoil
To view the contents of the log, you can use the cat command:
cat /opt/vCanopy/nginoil.log
Nginoil and CLI for Checking Your Servers Nginx Syntax
Due to the autohealing functions of Nginoil, we now also have commands that can help you check over the syntax issues that exist, and quickly restore symlinks to any sites that Nginoil may have removed once you’ve fixed their site-specific syntax errors.
With the commands below you can diagnose where issues exist.
Website Checks
The following command allows you to test a sites virtual server in isolation:
gp nginx -t site.url
You can also pass multiple domains:
gp nginx -t site1.url -t site2.url
Main and HTTP Context Checks
The following command allows you to test just the main context and http context of the nginx.conf file without any virtual servers:
gp nginx -t main
Test all main + http context + all virtual servers
Finally, this command tests them all one by one in isolation, outputting any issues found as it goes:
gp nginx -t all
Restore Symlinks: Bring Sites Back Online
f Nginoil has taken one or more of your sites offline due to syntax errors, you can use the following command to bring them back up once you have fixed them.
The following command will check a sites Nginx syntax and if there are no errors it will restore it’s virtual host symlink and bring the site back online (replace site.url with your site address):
gp nginx -t site.url -update-symlinks
This will run the test and if it passes then put the symlink back into the sites-enabled directory.
Update Symlink Flags
The following two flags can be added to any of the commands above:-update-symlinks -update-symlink
Additional Start, Restart, Reload Flags
The following flag can be added to the above commands start, restart, or reload Nginx in one go:-service-action {start||restart||reload}
Example Usage:
gp nginx -t site.url -service-action {start||restart||reload}
gp nginx -t domain.com -t another.com -update-symlinks -service-action reload
Nginoil and gp nginx reload
When you have a syntax error, running a regular reload like so:gp nginx reloadNginx won’t reload while a syntax error is present. However, you can add the
-apply-nginoil flag like so:
gp nginx reload -apply-nginoilThis will attempt to automatically fix any syntax errors and then reload. Now you will need to fix things, use the test commands, and put the symlinks back for any sites that were taken offline.